When it comes to addressing chronic knee pain or injury, there are various types of knee replacement surgery available. These surgeries are designed to alleviate discomfort, restore movement, and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions such as osteoarthritis or severe knee injuries. In this blog, we will break down the most common types of knee replacement surgery, including total, partial, robotic-assisted, minimally invasive, and revision knee replacements.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is a common procedure to help people with severe knee pain regain mobility and improve their quality of life. There are different knee surgeries, each tailored to a patient’s specific condition. Understanding these options can help you decide which procedure is best suited for your needs.
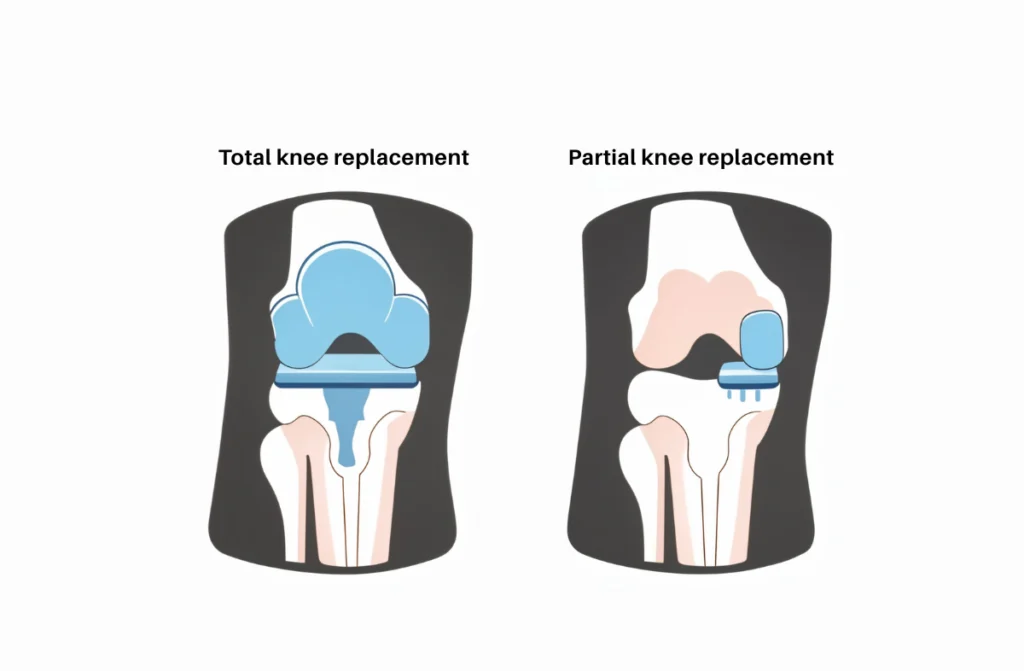
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total Knee Replacement (TKR) is one of the most common different knee surgeries performed today. It is typically recommended for patients with advanced osteoarthritis or severe knee damage where non-surgical treatments have failed to provide relief. During TKR, both sides of the knee joint are resurfaced with prosthetic implants, replacing the damaged cartilage and bone with metal and plastic components. This surgery is particularly effective for individuals experiencing chronic pain, stiffness, and difficulty in performing everyday activities like walking or climbing stairs.
The goal of TKR is to relieve pain, improve function, and restore range of motion in the knee. This type of surgery generally requires hospitalization for a few days, followed by physical therapy to rebuild strength and flexibility in the knee joint. Although the recovery time can be a few months, patients usually experience significant improvement in mobility and quality of life after a successful total knee replacement. TKR has a high success rate and can last for 15-20 years or longer with proper care.
Procedure
- Damaged cartilage and bone are removed.
- Artificial materials are used to replace the knee joint.
- General or spinal anesthesia is administered.
- Physical therapy is recommended post-surgery for recovery.
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce knee stress.
- Engage in regular exercise to strengthen knee muscles.
- Treat knee injuries early to avoid future complications.
- Follow a balanced diet to support joint health.
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial Knee Replacement is one of the types of knee replacement surgery. This procedure is recommended for patients whose knee damage is confined to one part of the knee, typically due to early-stage arthritis. Unlike TKR, which replaces the entire knee joint, a partial knee replacement involves only resurfacing the damaged section, preserving the healthy parts of the knee.
This surgery is less invasive than a total knee replacement, resulting in a shorter hospital stay, quicker recovery, and less postoperative pain. Since the majority of the knee remains intact, patients often retain more of their natural knee movement. However, partial knee replacement may not be suitable for patients with widespread arthritis or damage in multiple areas of the knee. Long-term success rates are also high, but there may be a need for revision surgery in the future if arthritis progresses to other parts of the knee.
Procedure
- Only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced.
- Healthy parts of the knee remain intact.
- Less invasive than total knee replacement.
- Requires a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery.
Prevention
- Regular exercise strengthens the knee joint.
- Avoid excessive strain on your knees.
- Early intervention in knee injuries can prevent worsening damage.
- Keep a healthy weight to reduce wear on the knee.
Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement
Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement is one of the newer and more advanced tjoint replacement surgery types. In this procedure, surgeons use robotic technology to assist in the precision of the surgery. The robot helps the surgeon plan and execute the procedure with higher accuracy, ensuring the artificial joint is aligned perfectly with the patient’s anatomy. This precision can lead to better outcomes in terms of pain relief, joint function, and longevity of the implant.
This type of knee replacement surgery can be applied to both total and partial knee replacements. The robot does not perform the surgery itself; rather, it assists the surgeon by providing real-time data and guiding the instruments. Robotic-assisted surgery often results in smaller incisions, less damage to surrounding tissues, and faster recovery times. It is especially beneficial for patients with complex joint conditions or those seeking a quicker return to normal activities.
Procedure
- The surgeon uses a robotic arm for precision.
- Cuts are made with greater accuracy.
- Artificial components are placed more precisely.
- Leads to better alignment and improved outcomes.
Prevention
- Stay active and exercise regularly to maintain knee health.
- Address injuries as soon as they occur.
- Get regular medical checkups to catch knee issues early.
- Maintain proper knee alignment through physical therapy.
What Are the Different Types of Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is performed to relieve chronic knee pain and mobility issues. There are several different knee surgeries, depending on the severity of the condition:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR) – Replaces the entire knee joint with an artificial implant.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR) – Only the damaged part of the knee is replaced.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement – Both knees are replaced simultaneously.
- Revision Knee Replacement – Performed to correct previous knee implants.
Choosing the best type of total knee replacement depends on factors such as age, lifestyle, and the extent of joint damage.
How Is a Total Knee Replacement Performed?
The joint replacement surgery types vary, but a total knee replacement follows these steps:
- Incision & Removal – The surgeon makes an incision and removes damaged cartilage.
- Implant Placement – Artificial components are positioned to mimic the knee’s function.
- Bone Resurfacing – The femur and tibia are reshaped for the prosthetic fit.
- Final Adjustments – The implant is secured, and the incision is closed.
This procedure restores knee stability and mobility effectively.
What Kind of Anesthesia Is Used in a Knee Replacement?
During a total knee replacement, anesthesia options include:
- General Anesthesia – The patient is completely unconscious during surgery.
- Spinal or Epidural Anesthesia – Numbs the lower body while keeping the patient awake.
- Regional Nerve Blocks – Provides additional pain relief post-surgery.
The best type of total knee replacement is often complemented by advanced anesthesia techniques for better pain management.
What Are Knee Replacement Implants Made Of?
Knee implants in different knee surgeries are made of durable materials, including:
- Metal Alloys (Titanium, Cobalt-Chromium) – Ensure strength and longevity.
- Medical-Grade Plastics (Polyethylene) – Provide smooth joint movement.
- Ceramic Components – Reduce wear and tear over time.
The best type of total knee replacement involves selecting high-quality implants for long-lasting performance.
Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement
Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement is another innovative approach to best type of total knee replacement. As the name suggests, this technique uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments to perform the surgery with minimal disruption to the surrounding muscles and tissues. This contrasts with traditional knee replacement surgery, where a larger incision is made, and more soft tissue is disturbed to access the knee joint.
This procedure can be used for both joint replacement surgery types and partial knee replacements, making it one of the versatile types of knee replacement surgery. Patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery typically experience less postoperative pain, a quicker recovery period, and reduced scarring. However, not all patients are candidates for this type of surgery, as it depends on factors such as the patient’s weight, bone structure, and severity of the knee damage. Despite these benefits, the surgeon must still achieve the same level of accuracy in placing the implant to ensure long-term success.
Procedure
- A smaller incision is made to access the knee.
- Less tissue is disturbed, leading to a quicker recovery.
- Prosthetic components are inserted through the small incision.
- Results in less post-surgery pain compared to traditional methods.
Prevention
- Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling.
- Maintain a healthy diet to keep your joints in good condition.
- Avoid high-stress activities that strain the knee joint.
- Use proper body mechanics when lifting or exercising.
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision Knee Replacement is a procedure performed when a previous knee replacement has failed or worn out over time. While best type of total knee replacement are successful and last many years, some patients may require revision surgery due to implant loosening, infection, or wear-and-tear. This type of surgery is more complex than a primary knee replacement, as the surgeon must remove the old prosthetic components and replace them with new ones.
Revision knee replacement can be more challenging due to scar tissue, weakened bone, or other complications that may have developed since the original surgery. Patients undergoing revision surgery may have a longer recovery time and may require additional rehabilitation. Despite the challenges, revision surgery can still provide relief from pain and restore knee function, though the success rate may vary depending on the patient’s overall health and the condition of the knee.
Procedure
- Old or worn-out components are removed.
- New prosthetic components are inserted.
- Requires specialized surgical expertise due to complexity.
- Post-surgery recovery may take longer than initial knee replacement.
Prevention
- Attend regular checkups to monitor knee joint health.
- Follow all post-surgery care instructions closely.
- Keep your weight in a healthy range to avoid stressing the joint.
- Avoid high-impact activities that may damage the replacement.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as joint replacement surgery, is a procedure that involves replacing a damaged or worn-out knee joint with an artificial one. The surgery is typically recommended for individuals suffering from chronic knee pain due to arthritis, injury, or other joint diseases. By removing the damaged portions of the knee and replacing them with durable prosthetic components, the surgery aims to restore mobility, reduce pain, and improve overall quality of life. Knee replacement surgery is one of the most common surgeries performed to treat joint pain, allowing individuals to regain their ability to perform daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and participating in physical exercise.
To support long-term recovery and joint health, incorporating best foods for joint health such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts into your diet can help reduce inflammation and promote healing after the procedure.
How is the Surgery Performed?
Knee replacement surgery involves several key steps to ensure the successful implantation of the artificial knee joint. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes about 1-2 hours. Here’s a breakdown of how the surgery is performed:
- Preparation: The surgeon makes an incision in the knee area to access the joint.
- Removing damaged tissue: The damaged or diseased parts of the knee, including cartilage and bone, are removed.
- Implantation: The artificial components, typically made from metal, plastic, and ceramic materials, are then placed in the knee.
- Closure: Once the new knee is in place, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures, and the joint is carefully realigned.
After surgery, best foods for joint health can assist in reducing inflammation, enhancing recovery, and supporting the healing process. Including different knee surgeries such as partial or total knee replacement can offer alternatives based on the severity of joint damage.
What is the Recovery Time?
Recovery from knee replacement surgery varies for each individual, depending on factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to post-surgery rehabilitation. Generally, the recovery time can be broken down as follows:
- Initial Recovery: Most patients can expect to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days after surgery, during which they will start physical therapy to improve mobility.
- Short-Term Recovery: Within 2-3 weeks, patients can begin walking with the aid of a walker or cane. Swelling and discomfort may persist, but this is normal.
- Full Recovery: Full recovery can take anywhere from 3-6 months, during which patients continue with physical therapy to restore strength and function.
Incorporating best foods for joint health like omega-3 rich fish, olive oil, and antioxidants can speed up recovery. Additionally, it’s important to note that joint replacement surgery types vary in terms of recovery times, with partial replacements often requiring shorter recovery periods than full knee replacements.
By focusing on proper nutrition, including the best foods for joint health, and following post-surgery guidelines, you can optimize your recovery and restore joint function efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of knee replacement surgery can help you choose the best option for your specific condition. Whether you’re considering total knee replacement, partial knee replacement, or robotic-assisted surgery, it’s important to discuss all your options with your doctor. Each type of surgery offers unique benefits, depending on your needs. If you’d like more information or want to schedule a consultation, don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to help you make the best decision for your knee health.
