Sudden Cardiac Arrest is a critical medical emergency that occurs without warning and demands immediate attention. CTS Specialty Hospital has been at the forefront of treating this condition, offering world-class care and advanced medical interventions. Understanding Sudden Cardiac Arrest, its symptoms, causes, and treatment can save lives and prepare individuals to respond effectively. Let’s dive into the essential details of this life-threatening event.
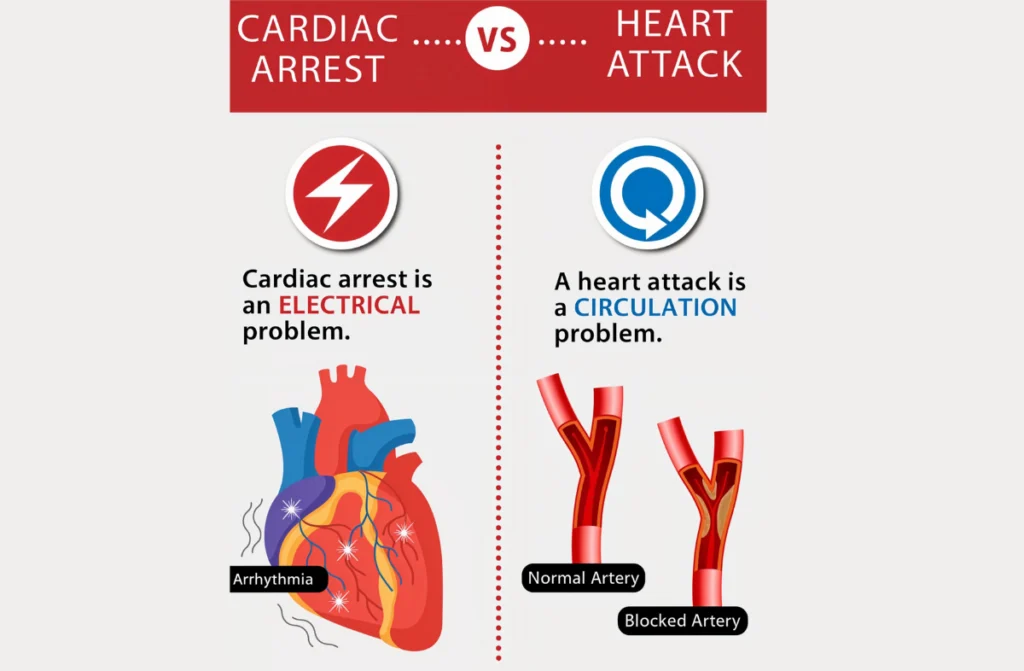
What is Cardiac Arrest?
Sudden Cardiac Arrest happens when the heart abruptly stops beating, preventing blood from flowing to the brain, lungs, and other vital organs. It’s different from a heart attack, which is caused by blocked blood flow to the heart. Sudden Cardiac Arrest requires immediate medical intervention to restore the heart’s rhythm and prevent fatal outcomes.
How Common is Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest is more common than many people realize. It affects thousands of individuals every year across the globe, with many cases occurring outside of hospitals. Quick access to emergency medical care, such as that provided by CTS Specialty Hospital, significantly improves survival rates.
Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Recognizing the symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden Collapse: The person may lose consciousness without any warning.
- No Pulse: The heart stops beating effectively, leading to an absence of a detectable pulse.
- No Breathing: The person may stop breathing or have gasping breaths.
- Chest Pain: Though less common, chest discomfort can occur before the arrest. Chest Pain in Children, although rare, can also be a symptom to watch for in certain cases.
If you observe these symptoms, call emergency services immediately and begin CPR if trained.
Causes of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Several factors can trigger Sudden Cardiac Arrest. These include:
- Heart Disease: Conditions like coronary artery disease can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Electrical Disorders: Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can disrupt the heart’s function.
- Congenital Heart Defects in Children: These are structural problems in the heart present from birth that can sometimes lead to cardiac arrest.
Chest Pain in Children: Could It Be Serious?
Chest Pain in Children is often not linked to the heart but can still be concerning. Common causes include:
- Muscle strain or injury.
- Respiratory infections causing chest discomfort.
- Rarely, Congenital Heart Defects in Children may cause chest pain.
It’s essential to monitor any persistent or severe symptoms and consult a doctor if needed.
Risk Factors for Cardiac Arrest
Understanding the risk factors helps in prevention. Key risk factors include:
- Age and Gender: Older adults and males are at higher risk.
- Family History: A family history of cardiac issues increases the likelihood.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity are significant contributors.
Can Children Have Heart Attacks?
Though rare, Can Children Have Heart Attacks is a question that raises concern among parents. Children can experience heart attacks, often due to Congenital Heart Defects in Children or other underlying conditions. Recognizing symptoms such as sudden chest pain, difficulty breathing, or fainting is essential.
Potential Signs in Children
Parents should look for:
- Sudden chest discomfort or tightness.
- Shortness of breath during physical activity.
- Unexplained fainting episodes.
Complications of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
The complications of Sudden Cardiac Arrest are severe and life-threatening. Without immediate treatment, it can result in:
- Brain Damage: Prolonged lack of oxygen can lead to irreversible brain injury.
- Death: Sudden Cardiac Arrest is fatal in most cases if not treated quickly.
Diagnosing Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Diagnosis typically occurs during the emergency response. Doctors use various tools and tests to determine the cause and severity:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Identifies irregular heart rhythms.
- Blood Tests: Check for underlying heart conditions.
- Imaging Tests: Advanced scans may reveal structural heart issues or Congenital Heart Defects in Children.
Detailed Testing in Children
For children showing signs of cardiac distress, specialized testing can include:
- Echocardiography to examine heart structure.
- Stress tests to measure heart function during activity.
- Genetic testing to identify inherited heart conditions.
Treatment for Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Treatment for Sudden Cardiac Arrest involves immediate and long-term measures:
- CPR and Defibrillation: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation and using a defibrillator restore the heart’s rhythm.
- Hospital Care: Experts provide advanced treatments, such as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) and medications.
What Should I Do About My Child’s Chest Pain?
If your child experiences unexplained chest pain:
- Seek Immediate Care: Visit a healthcare provider to rule out serious conditions.
- Monitor Symptoms: Note if the pain worsens with activity or persists.
- Get Expert Help: Early intervention is critical, especially in cases involving Congenital Heart Defects in Children.
Understanding Congenital Heart Defects in Children
Congenital Heart Defects in Children are abnormalities in the heart’s structure present from birth. These defects vary in severity and type but can sometimes cause Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
Types of Congenital Heart Defects in Children
The common types include:
- Septal Defects: Holes in the heart’s walls.
- Valve Abnormalities: Malfunctioning heart valves affecting blood flow.
- Complex Defects: Combination of multiple structural issues.
Preventing Complications
Early diagnosis and regular medical checkups are key to managing Congenital Heart Defects in Children effectively. Interventions may include:
- Surgical repairs for structural defects.
- Medications to regulate heart function.
- Ongoing monitoring to prevent long-term complications.
Preventing Sudden Cardiac Arrest
While it’s not always preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Regular Checkups: Routine screenings for heart health.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking.
- Managing Medical Conditions: Controlling conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes.
The Importance of Awareness
Understanding the symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest and the associated risks, such as Congenital Heart Defects in Children, can save lives. Being proactive in seeking medical care, especially for Chest Pain in Children or questions like Can Children Have Heart Attacks, is crucial.
Tips for Staying Heart-Healthy
- Exercise Regularly: Cardiovascular fitness can reduce the risk of Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
- Eat Heart-Friendly Foods: Include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in your diet.
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking significantly increases cardiac risks.
Support for Families
Families dealing with cardiac conditions in children require emotional and practical support. CTS Specialty Hospital provides resources and guidance to help families navigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Sudden Cardiac Arrest is a life-threatening event that requires swift action and expert care. CTS Specialty Hospital is dedicated to saving lives through advanced diagnostics and treatment options. If you or your loved ones experience any symptoms or have concerns about heart health, don’t hesitate to reach out.Taking proactive measures is crucial. From routine checkups to managing chronic conditions, prioritizing heart health can make a difference. For families, understanding the risks of conditions like Congenital Heart Defects in Children and addressing issues such as Chest Pain in Children promptly is vital. Ensuring the right care at the right time can save lives and improve outcomes significantly
