Liver cancer is a growing concern among women worldwide. Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females can help in early detection, prevention, and timely treatment. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and prevention tips, ensuring every woman is equipped with essential knowledge to maintain liver health.
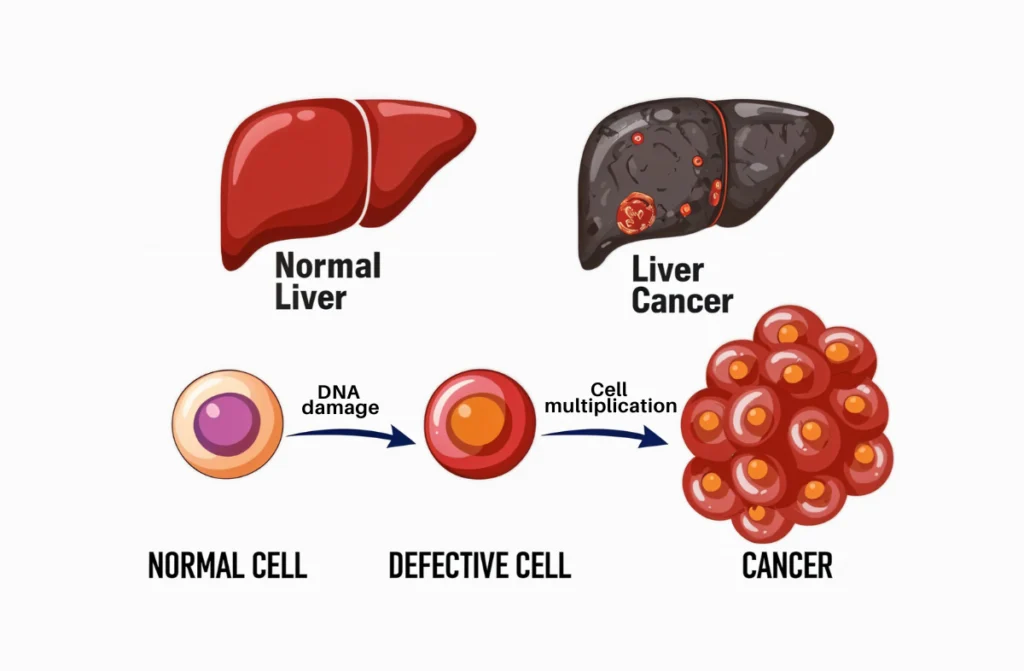
What Exactly is Liver Cancer?
causes of liver cancer in females is a condition where abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the liver. The liver, an essential organ, processes nutrients, removes toxins, and produces bile to help digest food. When its cells become cancerous, it disrupts these vital functions.
Types of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer can be categorized into:
1. Primary Liver Cancer
- Originates in the liver itself.
- Common types include:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Most common in adults.
- Cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer): Affects the bile ducts.
2. Secondary Liver Cancer
- Starts in another part of the body and spreads to the liver.
Women-Specific Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
Certain factors increase a woman’s risk of developing causes of liver cancer in females. These include:
- Hormonal changes: Estrogen may influence liver cancer progression.
- Chronic viral infections: Hepatitis B and C are major culprits.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Associated with fatty liver disease.
- Menopause and obesity: Hormonal shifts and weight gain can increase risk.
Common Early Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Early detection is critical. Women experiencing any of the following symptoms should consult a doctor:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal swelling or pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Nausea or vomiting
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a difference in successful treatment.
Top 7 Causes of Liver Cancer in Females
Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females can aid in better prevention and management. Here are the most common causes:
Chronic Hepatitis Infections
Hepatitis B and C infections are leading causes of liver cancer. These viruses can lead to chronic liver inflammation and scarring, significantly increasing the risk of cancer over time.
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake is a major risk factor. It damages liver cells, causing cirrhosis—a condition that predisposes the liver to cancerous changes.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, is a growing cause of liver cancer in females. It results in fat accumulation in the liver, leading to inflammation and scarring.
Exposure to Aflatoxins
Aflatoxins, toxins produced by molds found on improperly stored grains and nuts, can damage the liver. Long-term exposure significantly raises the risk of developing liver cancer.
Diabetes and Obesity
Females with diabetes or obesity are at higher risk of liver cancer due to the metabolic changes these conditions cause, including insulin resistance and chronic inflammation.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal imbalances, particularly with long-term use of oral contraceptives, have been linked to a slightly increased risk of liver tumors, some of which can turn cancerous.
Family History and Genetics
A family history of liver cancer or inherited liver disorders like hemochromatosis increases susceptibility, particularly in females with other risk factors. Understanding these causes can help in answering how can liver cancer be prevented through early detection and proactive prevention. Regular screenings, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical advice promptly are key steps in reducing the risk of liver cancer in females.
Managing conditions like hepatitis, obesity, and diabetes, as well as avoiding alcohol abuse and exposure to toxins, can significantly lower the likelihood of developing liver cancer. Early intervention is critical, so staying informed and consulting healthcare professionals regularly is essential.
How is Liver Cancer Diagnosed?
Doctors use various methods to diagnose liver cancer:
- Blood Tests
- Measure liver function and check for tumor markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP).
- Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to detect abnormalities.
- Biopsy
- A small liver tissue sample is taken for lab analysis.
Early and accurate diagnosis improves treatment outcomes.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer in Women
The treatment plan depends on the stage and type of liver cancer. Common treatments include:
- Surgery
- Partial liver resection or liver transplant for eligible patients.
- Ablation Therapy
- Uses heat or cold to destroy cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy
- Targets and kills cancer cells with high-energy rays.
- Chemotherapy
- Drugs to shrink or eliminate tumors.
- Targeted Therapy
- Medications that focus on specific cancer cells, sparing healthy tissue.
Preventing Liver Cancer: Practical Tips for Women
Preventing causes of liver cancer in females is possible by making informed lifestyle choices. Here are the tips for how to avoid liver cancer with some actionable steps:
- Avoid Hepatitis Infections
- Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B.
- Practice safe hygiene and avoid sharing needles.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Regular exercise and a balanced diet reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Stick to recommended guidelines or avoid alcohol altogether.
- Avoid Tobacco
- Quit smoking to lower the risk of liver and other cancers.
- Regular Screenings
- Women with risk factors should undergo periodic liver checkups.
These tips answer the questions how to prevent liver cancer, how to avoid liver cancer and how can liver cancer be prevented.” Taking these precautions can significantly reduce risk.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females is the first step in prevention and early detection. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying informed, women can protect themselves from this life-threatening disease. For expert care and guidance, contact CTS Hospital today. Our specialists are here to provide personalized advice and treatment options for liver health. Don’t hesitate—reach out to us now for more details!
